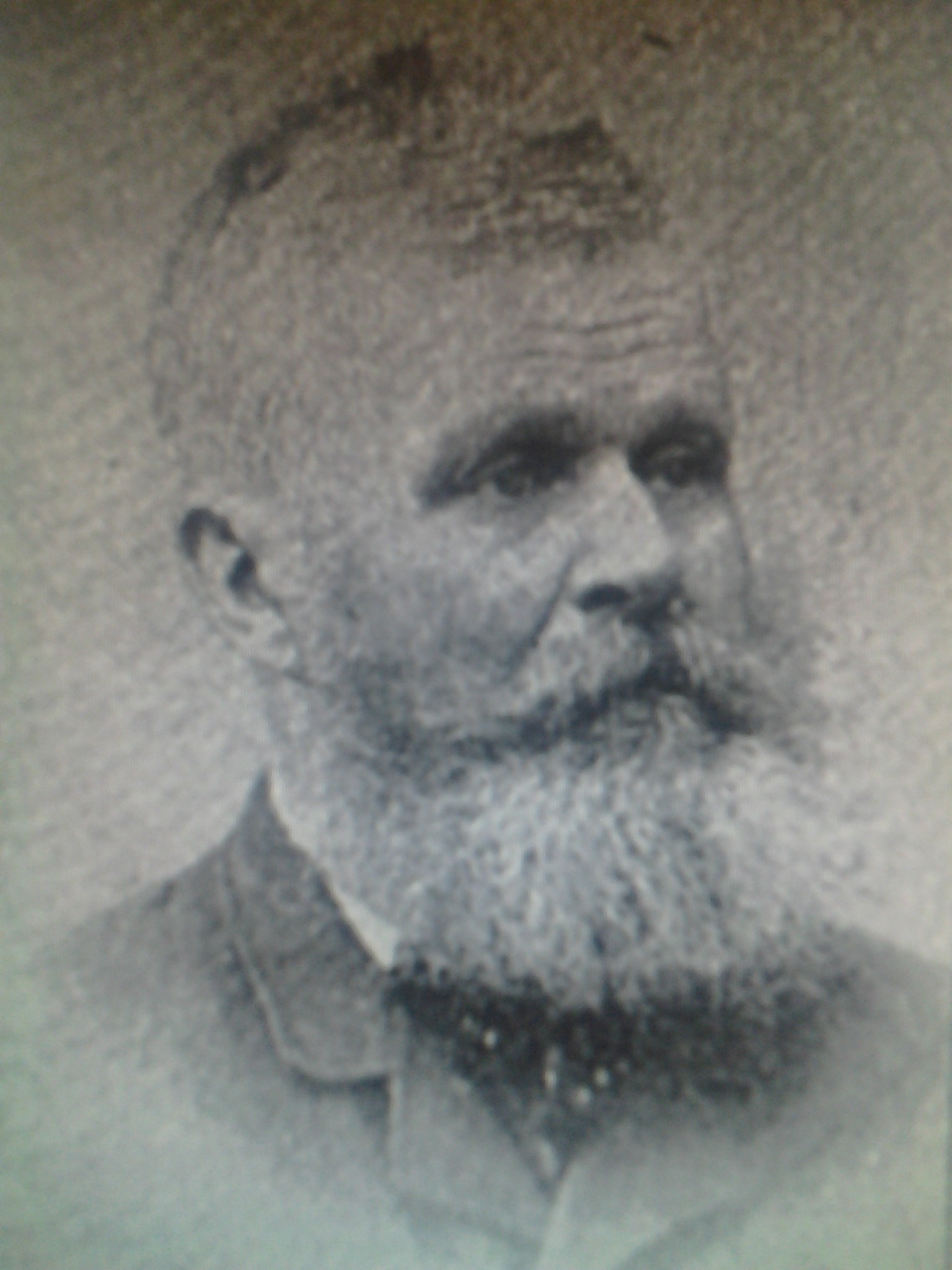
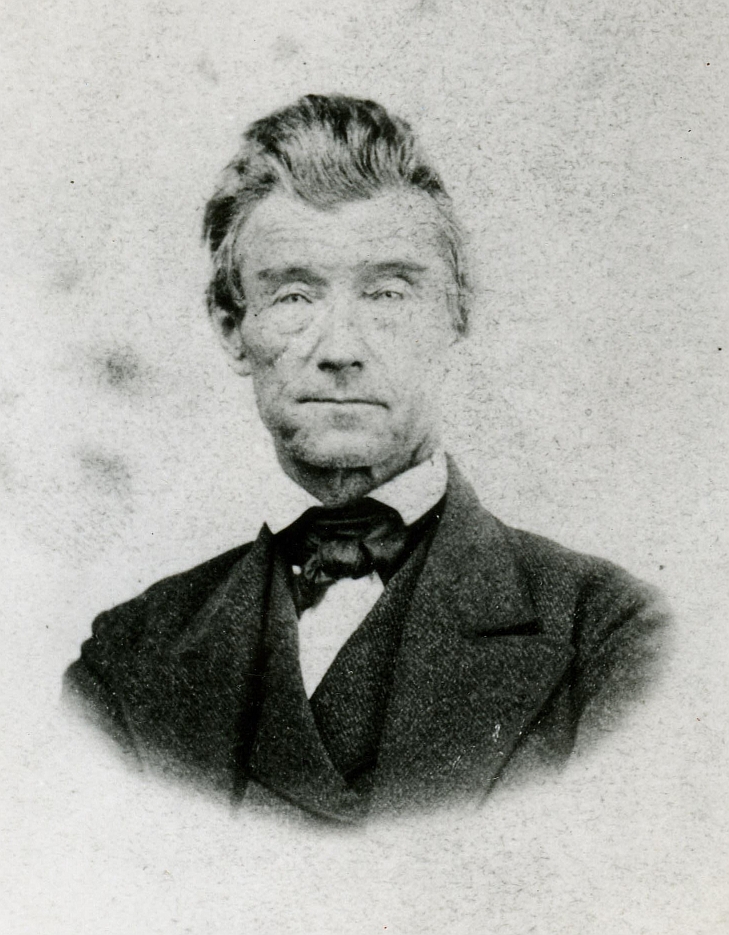
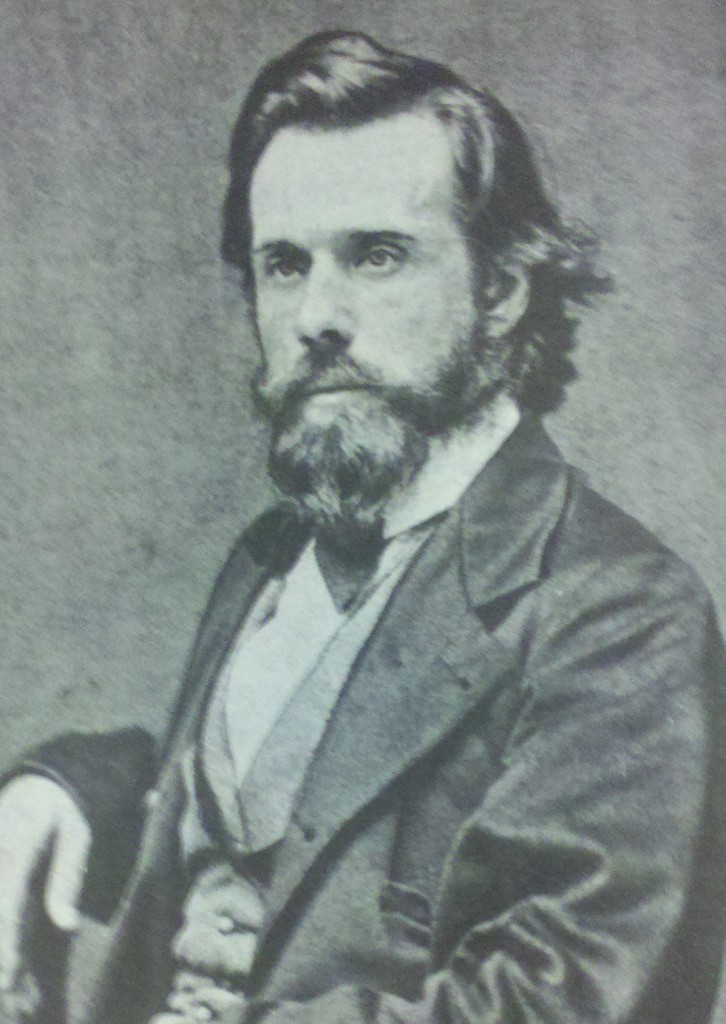
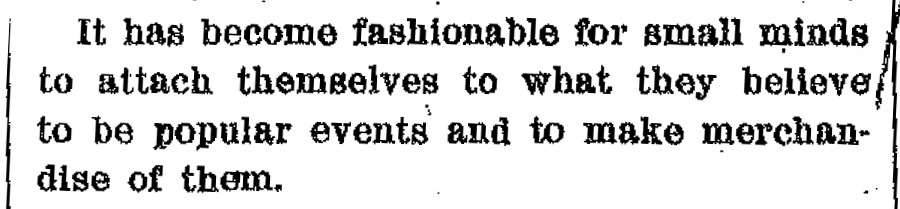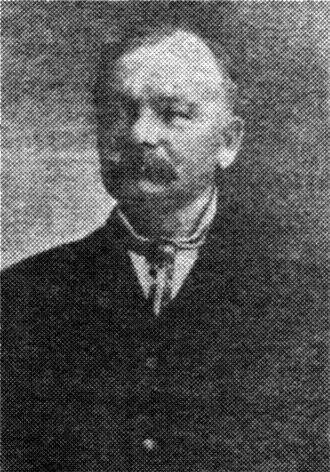Colonel Patrick Henry Winston
Colonel Patrick Henry WinstonFrom the desk of Steve Willis, Central Library Services Program Manager of the Washington State Library
The newspaper on microfilm reel grabbed at random this week holds a tale of “Colonel” Patrick Henry Winston and the Statue of Limitations. Yes, I meant to use the word “Statue” rather than “Statute.” You’ll see why.
“Colonel” Patrick Henry Winston, Jr. was born Aug. 22, 1847 in Windsor, North Carolina, the product of a family line that had also raised Patrick Henry, one of the great orators of the Revolution. Winston’s military rank was not bestowed by the Southern Army, nor was it an honorary title given by Kentucky. In any case he was indeed very briefly a soldier in the Confederacy during the last month of the Civil War. As it turned out, he was the sort of man who enjoyed embracing lost causes and relished the fight.
After being licensed to practice law in 1868, Winston seemed to have trouble finding a star to follow. Although he married and began a family that would eventually number ten children, it took him 20 years to find a city to settle in– Spokane. And it took him even longer to find a political party to call home. First a Democrat, then a Republican, then a Democrat, then a Silver Republican, then– after a bit it becomes too complicated to follow his allegiances. In the end he was a member of Patrick Henry Winston Party. But by 1896 he was part of the Populist Fusion ticket that swept every statewide office in Washington and he was elected the State Attorney General.

In addition to being politically active, Winston was a newspaperman. After his single term in office he started Winston’s Weekly, which ran 34 issues from Aug. 22, 1903 (Winston’s 56th birthday) to Apr. 9, 1904. To call it a newspaper is sort of misleading. Actually it was more of an ancestor to what we call blogs today. The paper gave him a forum to proclaim his views (such as advocating the U.S. takeover of Canada, or promoting the Right to Die), tell stories, and exhibit his devilish sense of humor.
John Rankin Rogers, who was elected Governor as part of the 1896 Populist sweep, switched to the Democratic Party in 1900 and was the only statewide incumbent to be re-elected. But only after less than a year into term two, he died in office Dec. 26, 1901. Soon there was talk of erecting a statue to honor the late Governor. Here’s how his former fellow Populist office-holder reacted to this news, Winston’s Weekly, Sept. 5, 1903:
THE ROGERS MONUMENT
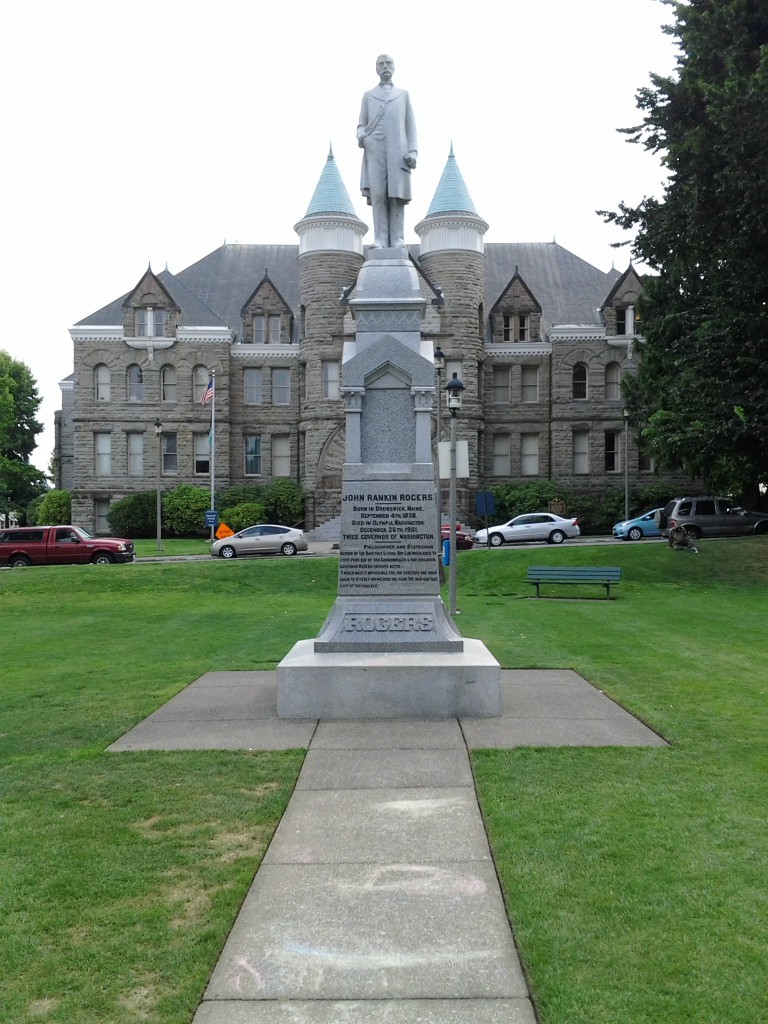 Statue of Governor Rogers
Statue of Governor Rogers“In all ages and in all lands monuments have been erected to perpetuate the memory of great deeds and great men.”
“The statue of Napoleon in his imperial robes surmounts the Vendome Column, that of Lord Nelson adorns Trafalgar Square, and a monument to the memory of Washington towers to the sky in the capital of the country of which he was the father. It is a beautiful custom, not only because it is a tribute to departed greatness and a grateful expression of popular gratitude, but because it is an object lesson calculated to inspire coming generations with lofty aspirations.”
“Happily for our country the names of many of her sons are worthy to be inscribed over the portals of immortal fame. Congress has provided a national pantheon in which may be placed by the states the statues of their illustrious dead, and in the Capitol grounds of many of the states there stand monuments erected by a grateful sovereignty to departed worth.”
“In selecting these subjects of a peoples gratitude and veneration the greatest care should be exercised lest what is now an honored and beautiful custom become one of derision and contempt.”
“The state of Illinois could with propriety erect a monument to Lincoln or Grant; Virginia to Washington, Jefferson, or Henry; Ohio to Wm. Tecumseh Sherman; Massachusetts to Samuel Adams; Pennsylvania to Benjamin Franklin; Oregon to Edward Baker; of Washington to General Isaac I. Stevens, her first governor, a brave pioneer, a distinguished statesman, and a gallant soldier.”
“Upon what theory is it proposed to erect a monument to perpetuate the memory of Governor Rogers? What was there in his life as a citizen or career as an office-holder to justify this greatest popular tribute? Except the fact that he happened to die in office, in what respect did his career differ from that of the ordinary run of governors? He was neither a statesman nor a soldier, nor a poet, nor an artist, nor an orator, nor an inventor, nor a discoverer, nor a philanthropist, nor a pioneer. Even as a druggist, which occupation he followed before entering the field of politics, he failed to make any revolution in the science of pharmacy, and although he wrote some ridiculous books which nobody remembers, he never took rank as an author. As a politician he failed to rise above the level of the every day populist politician of the Omaha platform school, beginning his political career by attacking corporations and ending it by soliciting railroad support. After posing as the champion of popular rights, when the opportunity came to go to the front in the fight against the merger, along with Governor Van Sant, he shrunk into pitiable littleness and played the role of a weak and nerveless trimmer.
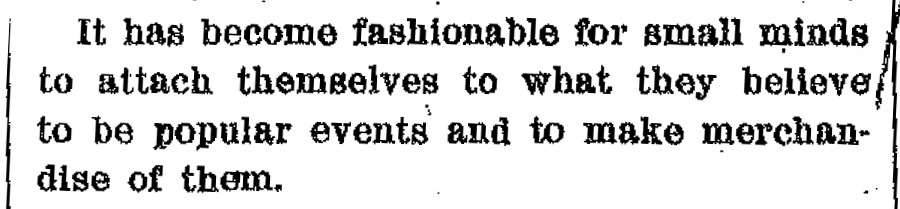 “It has become fashionable for small minds to attach themselves to what they believe to be popular events and to make merchandise of them.”
“It has become fashionable for small minds to attach themselves to what they believe to be popular events and to make merchandise of them.”
“After the exhibition furnished by the last legislature it seemed that the limit of human folly had been reached and that nothing could ever happen again to shock the common sense of the average person in the state of Washington, but the proposition to erect a monument by public subscription to the late Governor Rogers proves that there is no limit to human folly. If the falling political fortunes of these parasites will be temporarily propped by being attached to the remains of John R. Rogers that is no reason why whole communities should be involved in their folly and great state made ridiculous.”
 Winston’s 1899 Biennial Report
Winston’s 1899 Biennial ReportWinston died Apr. 3, 1904, and his newspaper died with him, the final issue assembled as a printed memorial by his friends. The Rogers statue was unveiled a few months later on the Capitol grounds, known today as Sylvester Park in downtown Olympia. Historian Gordon Newell commented in his book Rogues, Buffoons & Statesmen (1975):
“The body of John Rankin Rogers was buried in his home town of Puyallup, but the school children of the state donated their pennies and nickels to pay for a very bad statue of a good man and the lifesized figure of a frock-coated Rogers stands to this day in Sylvester park, its back to the old gray sandstone statehouse and its face toward a high-rise luxury hotel across from what used to be Main street. Carved in the granite base is the creed of the old Populist … ‘I would prevent the poor from being utterly impoverished by the greedy and avaricious … the rich can take care of themselves.'”
The Washington State Library has a complete run of Winston’s Weekly available on microfilm including via interlibrary loan as well as Winston’s Biennial Reports as Washington State Attorney General.
 also been appointed to the Land Office. During the time the above article was published, a petition had been circulating to remove Adams from the government position on grounds of incompetency. Adams’ response in print was to ask why anyone would “wish to deprive an old bullet-pierced soldier of the small pittance doled out to him after long years of hardship and danger …”
also been appointed to the Land Office. During the time the above article was published, a petition had been circulating to remove Adams from the government position on grounds of incompetency. Adams’ response in print was to ask why anyone would “wish to deprive an old bullet-pierced soldier of the small pittance doled out to him after long years of hardship and danger …”