Bill of Rights Day

From the desk of Rand Simmons
Vol. 1 no7 December 15, 2015
The Founding Fathers drafted the United States Constitution during the First Constitutional Convention, held from May through September 1787 in Philadelphia. The completed draft constitution, sent to the States for ratification in September 1787, did not include any mention of individual rights. The framers’ focus was largely on structuring a strong government, and getting that structure put into place. Without such a structure, the Founding Fathers feared the country’s collapse into chaos or new attacks from outsiders. They left the issue of individual rights without adding it to the Constitution during that meeting.
As a result of this omission, Edmund Randolph, George Mason, and Elbridge Gerry refused to sign the Constitution on principle. Maryland delegates, Luther Martin and John Francis Mercer reportedly walked out of the Convention, at least in part because the draft did not include a Bill of Rights. In September, Randolph, Mason and Gerry joined in asking for a second constitutional convention to address the issue of personal rights. All three men advocated strongly for a bill of rights throughout most of the constitutional convention. The people ultimately adopted the Constitution, sans any bill of rights, on September 17, 1787. Eleven states ratified it and it went into effect in 1789.
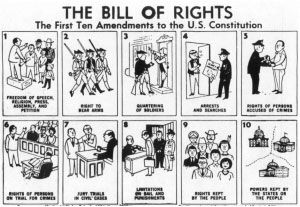 Image: Bill of Rights depicted in cartoon format from 1971 Young Citizen teacher’s guide transparency. Courtesy: Syracuse University. Found at Government Book Talk http://1.usa.gov/1QHOt32.
Image: Bill of Rights depicted in cartoon format from 1971 Young Citizen teacher’s guide transparency. Courtesy: Syracuse University. Found at Government Book Talk http://1.usa.gov/1QHOt32.Founding Father James Madison was a delegate from Virginia who had been a key actor and speaker at the First Constitutional Convention. He had held onto the idea of the individual freedoms as discussed at that Convention. Although Federalist Madison was originally a skeptic about needing a Bill of Rights, like Randolph, Mason and Gerry he came to believe that the inclusion of personal rights was imperative to be added to the United States Constitution.
The first ten amendments to the US Constitution are known as the “Bill of Rights.” Listen to retired Washington Chief Justice, Gerry Alexander, and nine others read these ten amendments.
“Enlightened statesman will not always be at the helm” (James Madison)
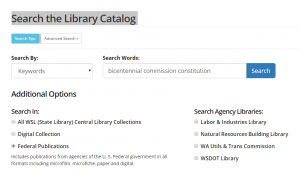
There are many federal publications about the United States Constitution and the Bill of Rights. To locate these in the State Library’s catalog set your Internet browser to http://www.sos.wa.gov/library/catalog.aspx.
Search the Library Catalog: Set Search By to keywords. In the Search Words box enter U.S. Constitution. Click on the Federal Publications radio button and press search.
The list of resources will tell you the collection in which the title is housed and give you it’s “call number” which indicates where it is located on the shelf.
Here are some other resources you may find useful:
- Ninth Judicial Circuit Historical Society. (1990). The Western frontiers of the Bill of Rights. Portland, Or: Ninth Judicial Circuit Historical Society.
- “This special issue of Western Legal History reflects the bitter-sweet story of the Bill of Rights in the American West”–P. [175] Published as the summer/fall 1990 issue of Western legal history, commemorating the 200th anniversary of the ratification of the Bill of Rights.Available at WSL:WSL Historic Research R 347.78 WESTERN 1990 v3 no2 LIB USE ONLY WSL Northwest Collection NW 347.78 WESTERN 1990 v3 no2
- Douglas, W. O. (1961). A living Bill of rights. Garden City, N.Y: Doubleday.
- Available at WSL:WSL General Collection 323.4 DOUGLAS 1961 WSL Governor’s Awards GWA DOUGLAS 1961 LIB USE ONLY
This publication was prepared by Rand Simmons, Federal Collection Executive Manager, with the assistance of Staci Phillips. For more information contact Rand [email protected].
You can follow any responses to this entry through the RSS 2.0 feed. Both comments and pings are currently closed.





