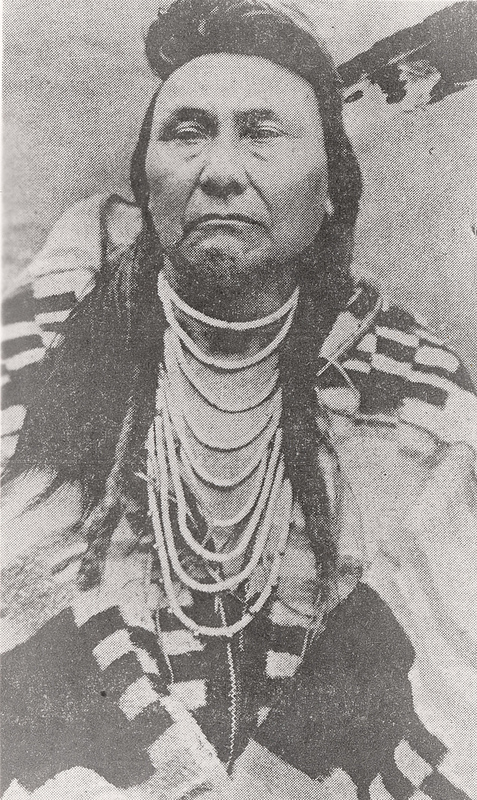
- Chief Joseph
Washington State Library continues to celebrate Native American Heritage month by focusing on the history of Chief Joseph and the Nez Perce.
The Nimi’ipuu (meaning “The Real People”) founded their villages in a 17 million acre swath of land that extended from the Bitteroot to the Blue mountains, especially along the banks of the Clearwater, Salmon, and Snake River drainages. Their language is a part of the Sahaptian sub division of the Penutian linguistic family found in the Western Plateau of North America. They had a wealth of resources in their mountainous home region but often migrated outside of ancestral lands to gather and hunt during certain seasonal cycles.
The Nimi’ipuu were dubbed Nez Perce (“pierced nose”) by French Candaian Fur Traders in the late 18th Century. The Nez Perce witnessed the explosion of European settlement that occurred in the very brief half century since their interactions with traders and explorers such as Lewis and Clark. With the Nez Perce Treaty of June 11, 1855, a portion of the Nez Perce leadership gathered at the Walla Walla Council signed away roughly 9.5 million acres of traditional lands (the treaty was ratified by the federal government March 8th and proclaimed on April 29th 1959), that relegated the tribes to the remaining 7.5 million acre reservation that spanned portions of the Idaho, Oregon and Washington Territories.
When gold was discovered in the region now known as Lewiston, ID, in 1860, the United States failed to maintain the terms of the treaty, leading to an influx of white settlers into Nez Perce Treaty lands. Three years later, a splinter group of the Nez Perce leadership signed away all but 75,000 acres of their ancestral lands. A large portion of the Nez Perce did not accept the validity of the treaty and refused to relocate to the acreage, located in Idaho, that was set aside. These non-treaty Indians included Chief Joseph, who stayed near his ancestral lands in Oregon’s Wallowa Valley. Tensions and violence between non-treaty Nez Perce and European settlers arose from the refusal of treaty demands for relocation. In June of 1877 Chief Joseph and other non-treaty leaders agreed to relocate to Fort Lapwai, ID, but a group of tribal members, outraged at past wrongs, attacked Idaho settlers in the Camas Prairie region. When Joseph arrived to the encampment and saw the devestation, he understood it as a declaration of war, realized an appeal for peace was futile, and began a fighting retreat across Idaho, Wyoming and Montana that ultimately deposited the fighting Nez Perce in Bear’s Paw Mountains of Montana, a short distance from the Canadian border.
On September 30, 1877, the United States Army’s Seventh Calvary, led by Gen, Nelson A. Miles, intercepted Joseph and the Nez Perce at Snake Creek in a surprise attack. The two forces fiercely fought throughout the three day stand-off until General Oliver Howard and his soldiers arrived, throwing the balance of forces off. On October 5, 1877 Chief Joseph surrendered, and in doing so, delivered a speech that, through interpretation by C.E.S. Wood, immortalized him. Instead of being sent to the Idaho reservation as promised by Gen. Miles, the non-treaty Nez Perce were sent to Fort Buford, KS under orders from commanding Army General William Tecumseh Sherman. Later they were transferred to live in a swampy section of Fort Leavenworth, KS and many tribe members contracted and perished from malaria. In 1879 Chief Joseph petitioned the President Rutherford B. Hayes and the Congress for relocation to Idaho or Indian Territory in present day Oklahoma. Due to rejection by Idahoans the band moved to Tonkawa, OK, where they remained until 1885 when they finally returned to the Pacific Northwest to join the Colville Reservation in Washington Territory. It is in the Collville lands that Chief Joseph passed away September 21, 1904.
The State Library has many resources on the celebrated leader and the Nimipu (Nez Perce) people including…
The story of Chief Joseph : from where the sun now stands / by Bruce A. Wilson. Okanogan, WA : Okanogan County Historical Society, [2006], c1960. R OVERSIZ 979.5004 WILSON 2006. In Library use only.
Chief Joseph & the flight of the Nez Perce : the untold story of an American tragedy / Kent Nerburn. First edition. New York, NY : HarperSanFrancicso, c2005. NW 970.3 NERBURN 2005.
Chief Joseph : guardian of the people / Candy Moulton. 1st New York : Forge, 2005. NW 979.5004 MOULTON 2005.
Chief Joseph, Yellow Wolf, and the creation of Nez Perce history in the Pacific northwest / Robert R. McCoy. New York : Routledge, 2004. NW 979.5004 MCCOY 2004.
Beyond Bear’s Paw : the Nez Perce indians in Canada / Jerome A. Greene. Norman : University of Oklahoma Press, c2010.
NW 971.0049 GREENE 2010.
Guide to the Nez Perce music archive : an annotated listing of songs and musical selections spanning the period 1897-1974 / by Loran Olsen. Pullman, Wash. : Washington State University, School of Music and Theatre Arts, 1989. WA 378.5 M971gui n 1989
Chief Joseph Interpretive Center / Confederated Tribes of the Colville Indian Reservation. [Nespelem, Wash.?] : Confederated Tribes, [1991?] WA 719.3 P231chi j 1991?
Collection on Dr. W. H. Faulkner, 1885. MS 383 This is a collection of negative photocopies of Dr. W. H. Faulkner’s reports concerning the transfer of the Nez Percé Indians to reservations in Colville, WA and Lapwaii, ID. The Indian Commissioner sent Dr. W. H. Faulkner, a special agent, to arrange the transfer and relocation of the Nez Percé Indians to the Pacific Northwest. Dr. Faulkner negotiated a compromise that divided the group. Some were to go to the Lapwaii, ID reservation and some to Colville, WA reservation.
Spalding Mission and Chief Joseph / by W.C. Jacks. [Lewiston, Idaho] : Printed by the Lewiston news, c1936. RARE 811.52 JACKS 1936
Nez Perce country : a handbook for Nez Perce National Historical Park, Idaho / produced by the Division of Publications, National Park Service. Washington, D.C. : U.S. Dept. of the Interior, 1983. I 29.9/5:121